Google BigQuery offers a streaming API which lets you insert data into BigQuery in near real-time and have it ready for analysis in no time.
Find the open source transformer code for this destination in the GitHub repository.
Getting started
RudderStack supports sending event data to BigQuery Stream via the following connection modes:
| Connection Mode | Web | Mobile | Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device mode | - | - | - |
| Cloud mode | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Once you have confirmed that the source platform supports sending events to BigQuery Stream, follow these steps:
- From your RudderStack dashboard, add the source. Then, from the list of destinations, select BigQuery Stream.
- Assign a name to the destination and click Continue.
Connection settings
To successfully configure BigQuery Stream as a destination, you will need to configure the following settings:
- Project ID: Enter your BigQuery project ID.
- Dataset ID: This is the ID of the project dataset for which you specified the Project ID above.
- Table ID: Provide the ID of the table into which you want to stream the event data.
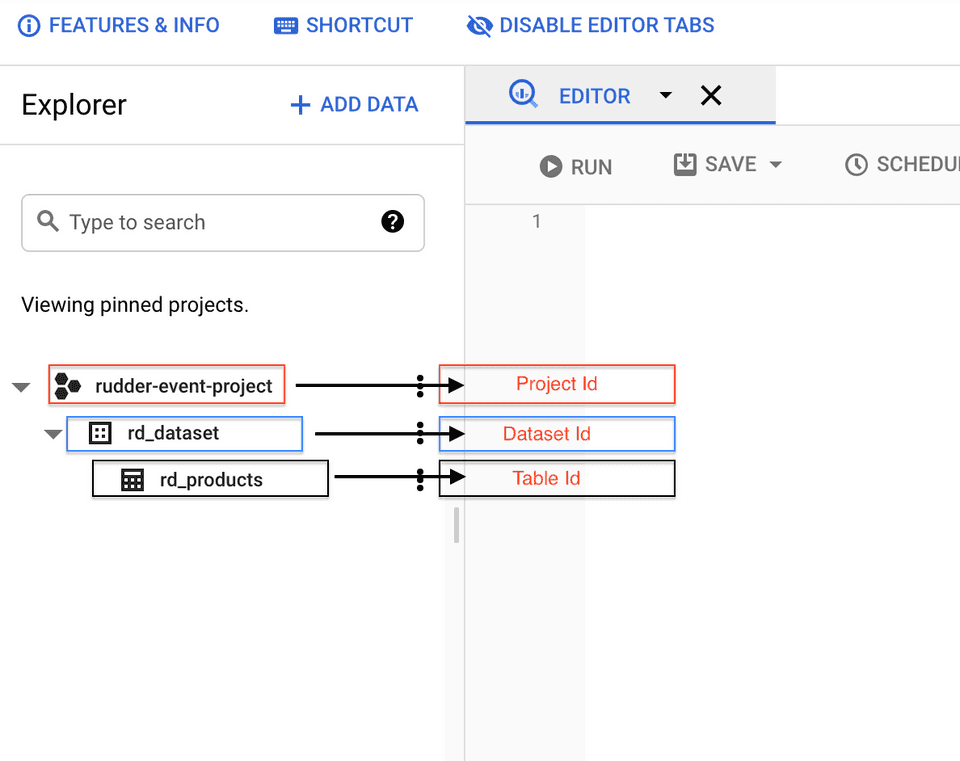
- Insert ID: This is an optional field. Enter the
insertIdused by Google to deduplicate the data sent to BigQuery. For more information on this setting, refer to the Deduplicating data section. - Credentials: Enter the contents of the credentials JSON you downloaded after creating your service account.
Sending events to BigQuery Stream
RudderStack supports sending only track events to BigQuery Stream. Make sure your track event payload format matches the table schema corresponding to Table ID specified in the dashboard settings.
templateSupportSuffix feature which creates a table schema during a streaming insert action.Suppose you want to stream the events from your web source to BigQuery and the table schema in your BigQuery dataset is as shown:
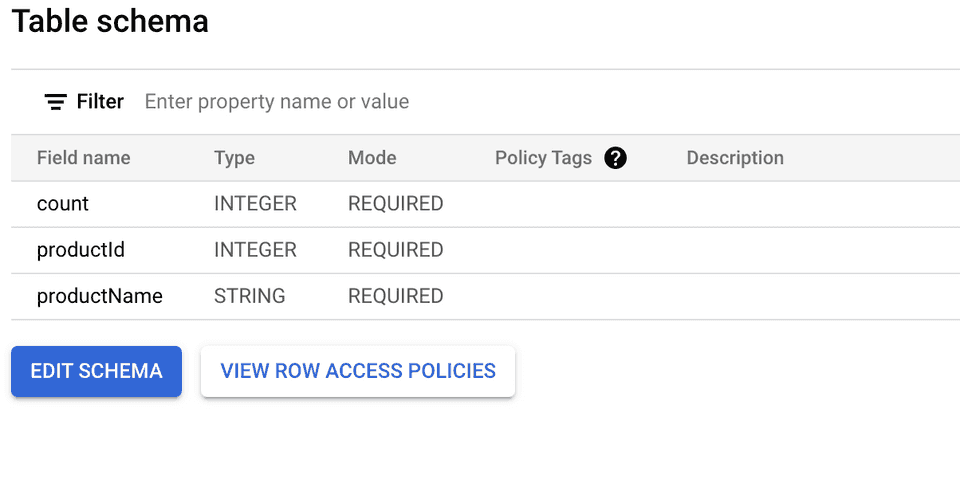
To successfully stream the events, the event tracked from your JavaScript SDK should look like the following:
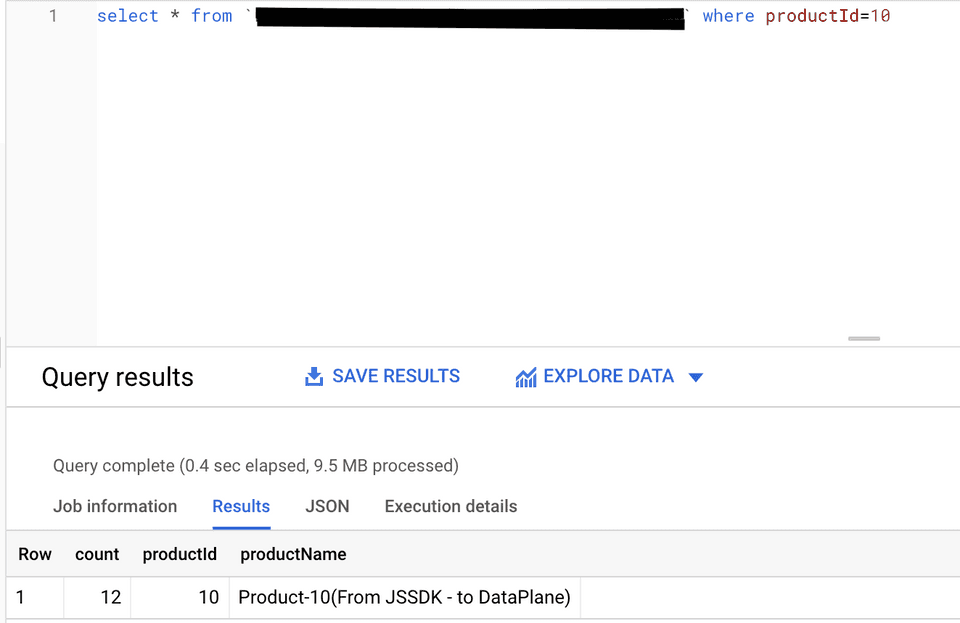
rudderanalytics.track("event", { productId: 10, productName: `Product-10`, count: 12});Note that the track properties in the above payload match with the fields specified in your table schema. Once streamed, you can view this event in your BigQuery console by running the following SQL command :
Deduplicating data
Google leverages the insertId to deduplicate the data sent to BigQuery. insertId is essentially an event property that uniquely identifies an event.
insertId.For more information on the deduplication process in BigQuery, refer to the BigQuery documentation.
Use case
Consider the following table schema:

When sending an Insert Product event to BigQuery, you can use the productId field to uniquely identify the product. Upon setting productId as the insertId, BigQuery uses it to deduplicate the data.
Dynamically configuring insertId
To dynamically configure insertId via the event payload, make sure that insertId is the column name present in your schema (or in the properties object in the event payload) used to uniquely identify an event.
Consider the following schema:

Suppose you have a dynamic configuration like {{ message.uniqueId || "productId" }} for the above schema. There are three cases to consider here:
Case 1: Unique ID is sent as a value which is not a key in the event properties
Consider the following payload:
{ "properties": { "productId": 212, "productName": "my product", "count": 24 }, ..., "uniqueId": <some_value> , ...}In the above case, deduplication is not applicable as the event properties do not contain <some_value> present in the payload.
Case 2: Unique ID is sent as a value which is a key in the event properties
Consider the following payload:
{ "properties": { "productId": 212, "productName": "my product", "count": 24 }, ..., "uniqueId": "productId", ...}In this case, deduplication is applicable as RudderStack sends the productId value (212) as the insertId to Google.
Case 3: Unique ID is not sent in the event payload
Consider the following payload:
{ "properties": { "productId": 212, "productName": "my product", "count": 24 }, ...}In this case, deduplication is applicable as RudderStack sends the productId value (212) as the insertId to Google.
If you use the dynamic destination configuration for insertId by passing a random value (e.g. 1234) in the above payload, deduplication will not be applicable as the properties object does not contain the value 1234.
Creating a service account
To create a service account in your Google Cloud Console, follow these steps:
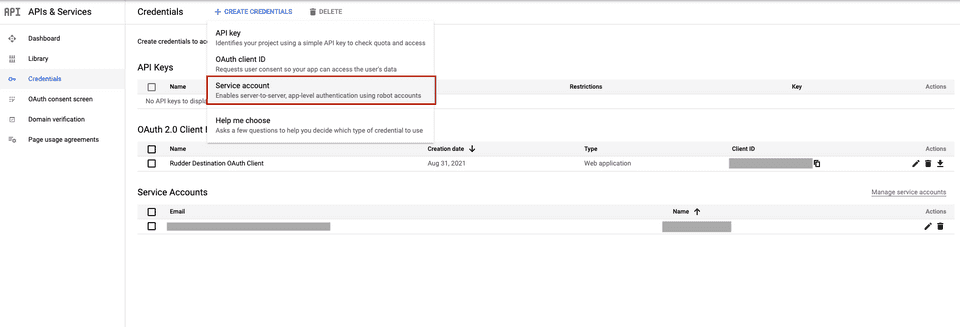
- In the left sidebar, go to APIs & Services > Credentials.
- Then, click CREATE CREDENTIALS > Service account, as shown:
- Enter the service account details and click CREATE AND CONTINUE.
- In the Select a role field, search and select the BigQuery Data Editor role and click CONTINUE.
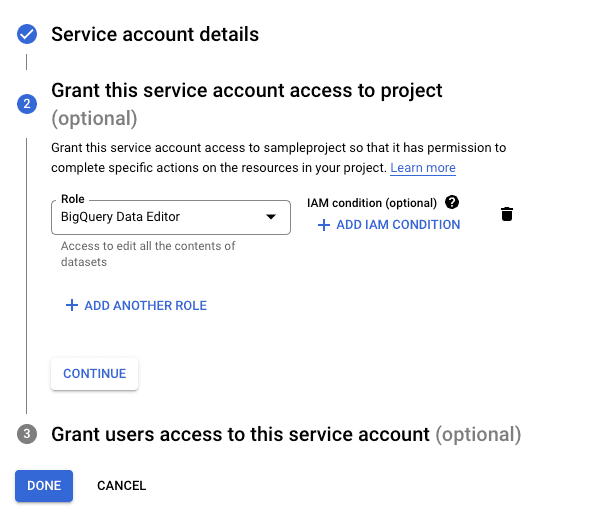
- Click DONE to finish the setup.
- Next, you need the service account credentials JSON required for RudderStack to send the data to BigQuery. To obtain this JSON, go to your service account.
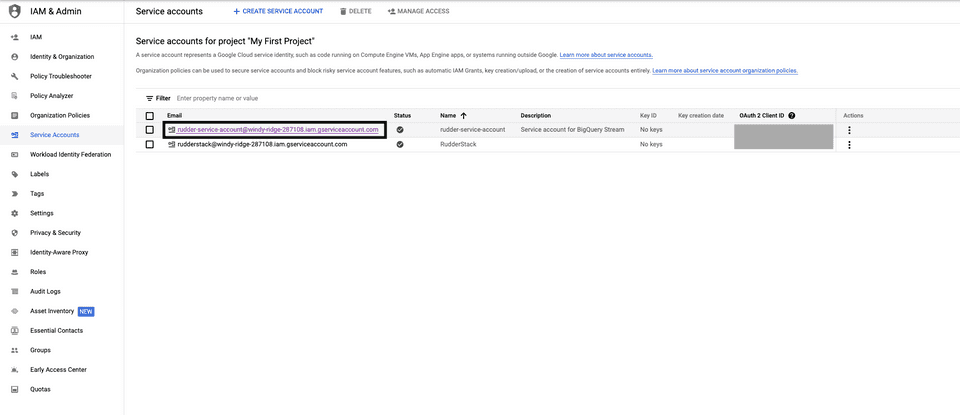
- Then, go to KEYS > ADD KEY > Create new key.
- Select the Key type as JSON and click CREATE.
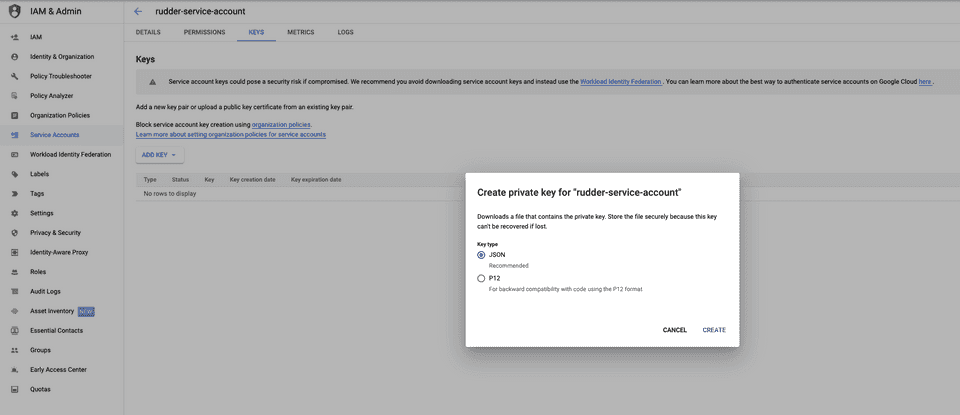
Your JSON key will be automatically downloaded. Copy and paste the contents of this JSON key in the Credentials field while configuring BigQuery Stream as a destination in RudderStack.
Troubleshooting
For the different error messages you might get when sending your event data to BigQuery Stream and their troubleshooting steps, refer to the BigQuery documentation.
Contact us
For more information on the topics covered on this page, email us or start a conversation in our Slack community.